In this blog, we will explore the critical differences between heart attacks and cardiac arrests, two potentially life-threatening conditions. Dr. S. Nagendra Boopathy provides insights into their symptoms, causes, and treatments, helping you to recognize these emergencies and react appropriately.
Introduction to Heart Conditions
Heart conditions encompass a range of disorders that affect the heart’s structure and function. These conditions can lead to severe complications, including heart attacks and cardiac arrests. Understanding the nuances of these conditions is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Heart diseases are often silent, developing over years without noticeable symptoms. Regular check-ups and awareness of risk factors can play a significant role in prevention.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, leading to damage. This blockage is usually caused by the buildup of fatty deposits in the coronary arteries, known as atherosclerosis.
Without sufficient blood supply, heart tissue begins to die, which can cause severe pain and other symptoms. Quick medical intervention is essential to restore blood flow and minimize heart damage.
Understanding Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It is often caused by an electrical disturbance in the heart that disrupts its pumping action, leading to a cessation of blood flow to the body.
Unlike a heart attack, which is a circulation problem, cardiac arrest is an electrical problem. Immediate CPR and defibrillation are critical to increase the chances of survival.
Causes of Heart Attack
- Atherosclerosis: The most common cause, where plaque builds up in the arteries.
- Coronary Artery Spasm: A temporary tightening of the muscles in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow.
- Risk Factors: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes increase the likelihood of a heart attack.
Understanding these causes can help in taking preventive measures. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can significantly reduce risks.
Causes of Cardiac Arrest
- Coronary Artery Disease: The leading cause, often linked to a heart attack.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Other Conditions: Heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, and congenital heart defects can also contribute.
Identifying these underlying conditions is vital for prevention. Regular cardiac evaluations can aid in early detection and management.
Symptoms of Heart Attack
- Chest Pain: Often described as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, or fullness.
- Shortness of Breath: This may occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Other Signs: Symptoms can include cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness.
Recognizing these symptoms can be lifesaving. If someone is experiencing these signs, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Symptoms of Cardiac Arrest
Recognizing the symptoms of cardiac arrest is crucial for immediate action. The signs can be sudden and dramatic, often occurring without warning.
- Sudden Collapse: The person may fall to the ground unexpectedly.
- Unresponsiveness: They will not respond to any stimuli, including shouting or shaking.
- No Breathing: Check for breathing; if they are not breathing or only gasping, this is a critical sign.
- Pale or Bluish Skin: This indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood.
Immediate recognition of these symptoms can significantly impact survival chances. Call emergency services without delay if you suspect someone is experiencing cardiac arrest.
Treatment for Heart Attack
Treating a heart attack quickly is vital to prevent further damage to the heart muscle. The approach may vary based on the severity and type of heart attack.
- Medications: Aspirin, thrombolytics, and antiplatelet agents are commonly used to dissolve clots and improve blood flow.
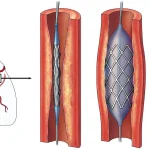
- Angioplasty: A procedure where a balloon is used to open blocked arteries, often followed by placing a stent to keep the artery open.
- Coronary Bypass Surgery: In severe cases, this surgery reroutes blood around blocked arteries.
Post-treatment lifestyle changes are essential. A heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can help prevent future incidents.
Treatment for Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest requires immediate intervention to restore normal heart activity. The treatment protocol is straightforward but must be executed quickly.
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): Perform chest compressions immediately to maintain blood circulation.
- Defibrillation: Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) as soon as possible to deliver an electric shock to the heart.
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS): Emergency medical personnel may administer medications and advanced interventions upon arrival.
Timely action can mean the difference between life and death. Encourage bystanders to assist with CPR and to seek emergency help.
Preventive Measures for Heart Health
Maintaining heart health is pivotal in preventing both heart attacks and cardiac arrests. A proactive approach can significantly reduce risk factors.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular screenings can help detect issues early.
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing saturated fats and sugars.
- Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking greatly reduces heart disease risk.
- Manage Stress: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can be beneficial.
Implementing these preventive measures can foster a healthier lifestyle and minimize the risk of heart-related emergencies.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between heart attack and cardiac arrest is essential for prompt and effective action. Recognizing symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and implementing preventive measures play a crucial role in heart health.
Education and awareness can empower individuals to act swiftly in emergencies, ultimately saving lives. Prioritize heart health, and encourage others to do the same.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
A heart attack is primarily a circulation issue caused by blocked blood flow to the heart, while cardiac arrest is an electrical problem where the heart stops beating effectively.
Can a heart attack lead to cardiac arrest?
Yes, a heart attack can trigger cardiac arrest, as the damage to heart tissue can disrupt its electrical signals.
How can I recognize a heart attack in women?
Women may experience atypical symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, or back pain, in addition to the more common symptoms of chest pain and shortness of breath.
What should I do if I see someone collapse?
Call emergency services immediately, check for responsiveness and breathing, and begin CPR if they are unresponsive and not breathing.
Is it possible to prevent heart disease?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.